Frangible Tank Roof Design
This paper presents the results of an investigation into the frangible joint behavior of tanks designed to api 650 rules.
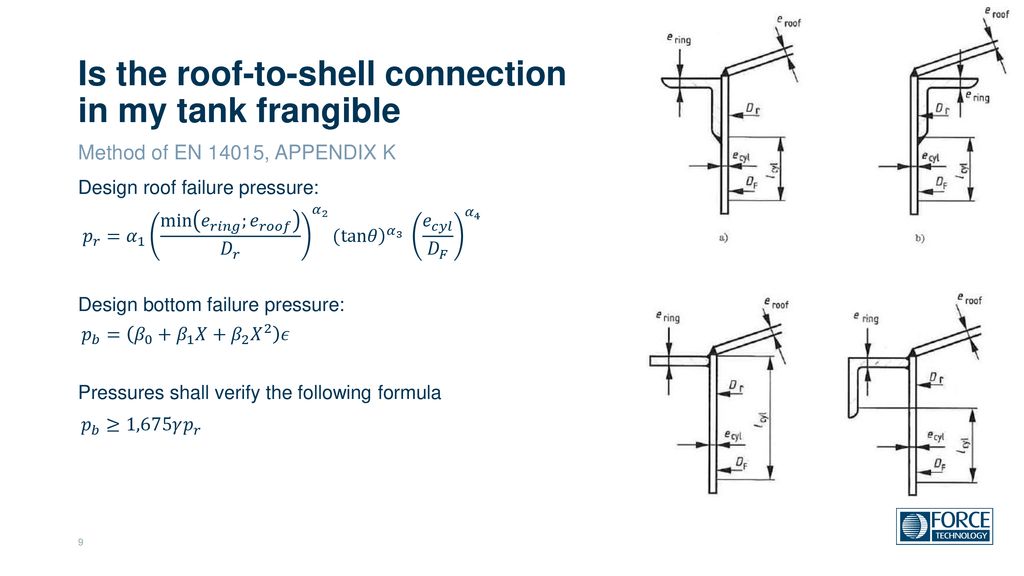
Frangible tank roof design. The api 650. This video documents the research and testing on frangible joint storage tanks performed at kansas state university and thunderhead engineering. In fact the frangible roof design fulfills the venting requirements due to deflagrations inside tanks for most tank sizes greater than about 35 feet in diameter. In the event of over pressurization the frangible roof to shell joint is designed to fail before the tank shell or the shell to bottom joint.
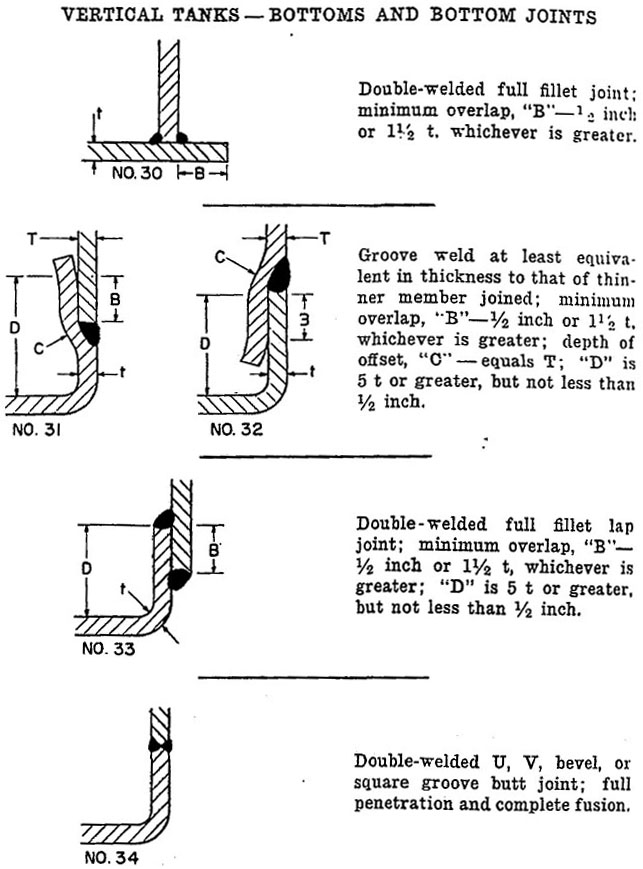
A frangible roof is a roof to shell joint or junction that is weaker than the rest of the tank and will preferentially fail if the tank is over pressurised. A frangible roof joint forming a flexible gastight connection between a tank shell and a roof comprising an annular link mechanism sealingly secured at or adjacent a first edge thereof to a rim of the tank and sealingly secured at or adjacent a second edge thereof to the periphery of the roof. In such tanks the roof to shell joint is intended to fail in the event of overpressurization venting the tank and containing any remaining fluid. Failure of the roof to shell junction can be expected to occur when the stress in the compression ring area reaches the yield point says f 6 calculated failure pressure.
F 4 1 establishes the maximum design pressure p for a tank that has been constructed or that has had its design details established. This failure is intended to vent the tank and contain any remaining fluid. Api 650 gives rules for the design of frangible roof joints in fluid storage tanks. A frangible roof joint forming a flexible gastight connection between a tank shell and a roof comprising an annular link mechanism sealingly secured at or adjacent a first edge thereof to a rim of.
The concept of frangible roof only applies to flat bottom cone roof tanks with limited roof apex angle.